Classification
Robust Tooling for Asset Management, Segmentation Taxonomy, Tags, and Change Control.
Classification
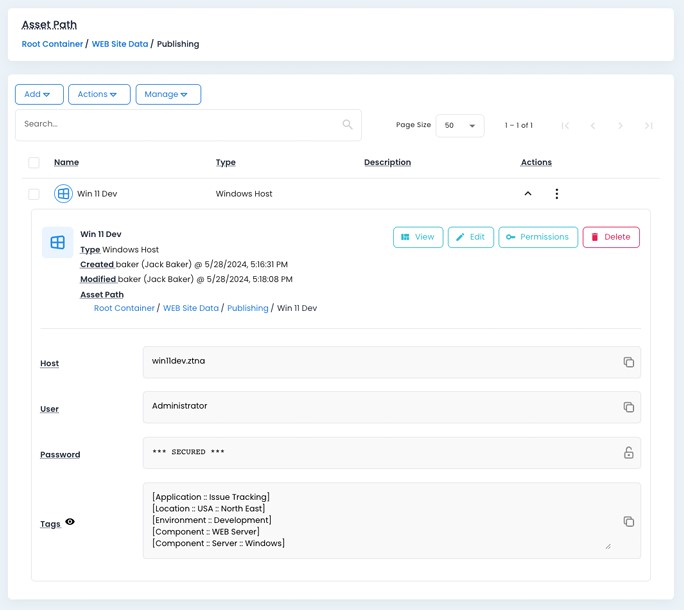
Asset management
The Asset database forms the core of microsegmentation operations, housing critical information such as asset access details, credentials, metadata, and classification tags. It supports delegated asset management through a hierarchical container tree, featuring role-based permissions, property inheritance, and REST API access.
Classification
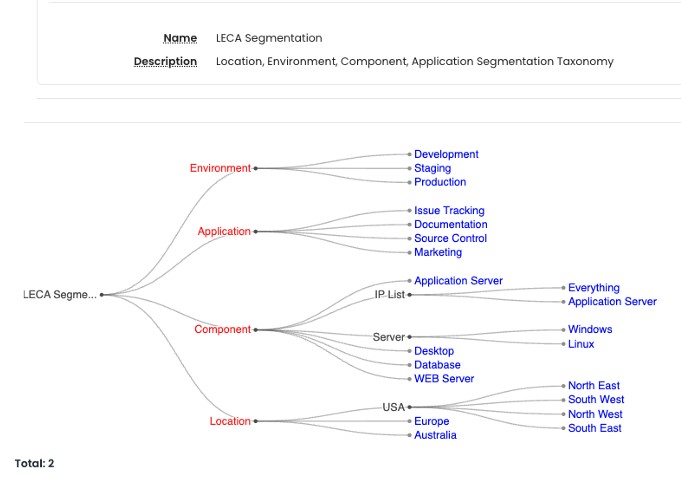
Segmentation Taxonomy
The Segmentation taxonomy is a structured hierarchy of business and technical terms that define the assets incorporated into our microsegmentation policies. These taxonomies can range from straightforward to intricate, encompassing descriptions of asset locations, environments, manufacturing stages, applications, components, or customized terms.
Classification
Tags
Our platform enables users to categorize assets using hierarchical segmentation taxonomy terms. By employing multiple values for asset tagging, it facilitates the creation of a comprehensive asset database. The flexibility to utilize multiple tagging fields across various segmentation taxonomies allows for experimenting with alternative segmentation strategies, enabling the division of networks into multiple segments in diverse configurations.
Intelligent tagging module enables term suggestions and mass tagging to facilitate maintenance of relevant and consistent asset classification.
Classification
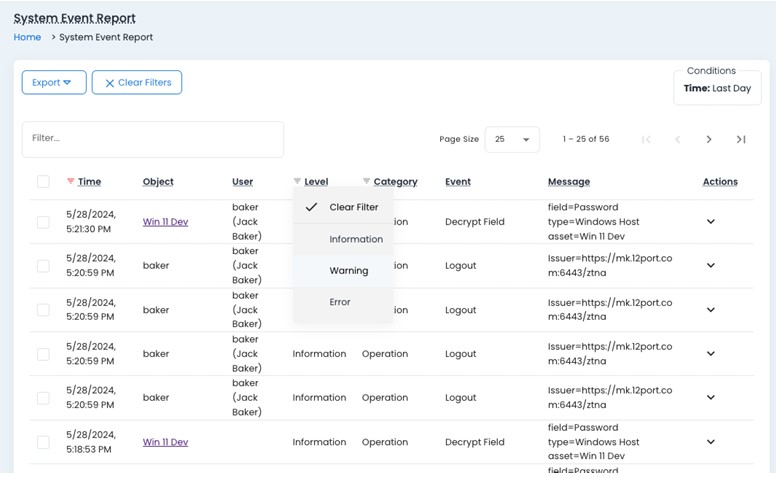
Change Control
The Asset database logs modification, tag addition, deletion, and configuration change of assets, policies, services, and other elements in an audit trail report. Each entry includes a timestamp and the user responsible for the change, ensuring compliance requirements are met. The change history feature tracks asset updates and tag evolution over time. A change approval cycle permits reviewing asset metadata and tagging updates before they are finalized and published in a segmentation policy.
Classification
Delegation
12Port allows delegation of asset management into hierarchically organized spaces, each with its own integrations, authentication, permissions, approval workflows, policies and taxonomies while inheriting parent space features to enforce centrally defined strategies down the space hierarchy. Further, each space organizes assets into nested container hierarchy with permissions inheritance. The hierarchical nature of the asset organization inside a tenant allows to involve more administrators to manage project- or location-based assets and networks.